什么场景
通常我们不会去获取一个已经隐藏的元素(这里隐藏指的是 display: none )的宽或高,原因是对元素的样式转化并不需要宽高去计算。
- 元素显示时,宽高来自样式
- 元素隐藏时,宽高对元素已没有意义(
display: none 不会占用空间)
我们如果想做一个元素高度的动画,这个动画的起始为0 结束这里不设置具体的高度,我们需要拿到元素的高度作为最终高度!问题是在元素高度为0的时候,我们无法拿到最终高度。
处理方法
先将元素显示,高度设置为 1px , visibility: hidden 但让元素不可见,当高度大于 1px 后,元素可见。
有什么方法获取元素高度
要先知道盒模型的概念:参考
height/width
height CSS 属性指定了一个元素的高度。默认情况下,这个属性决定的是内容区( content area)的高度,但是,如果将 box-sizing 设置为 border-box , 这个属性决定的将是边框区域(border area)的高度。
使用方式
`<div style="width: 100px"/>`;
element.style.width;
element.style.height;
这会直接获取元素的样式值,仅是 <div style="width: 100px"/>(这里的样式指设置的样式,并非最后解析完 css 的样式,不是 getComputedStyle 这种)。
我们很少使用该方法获取值,更多的是设置该值,来修改元素的内联样式(优先级更高),达到调整元素宽高的效果。
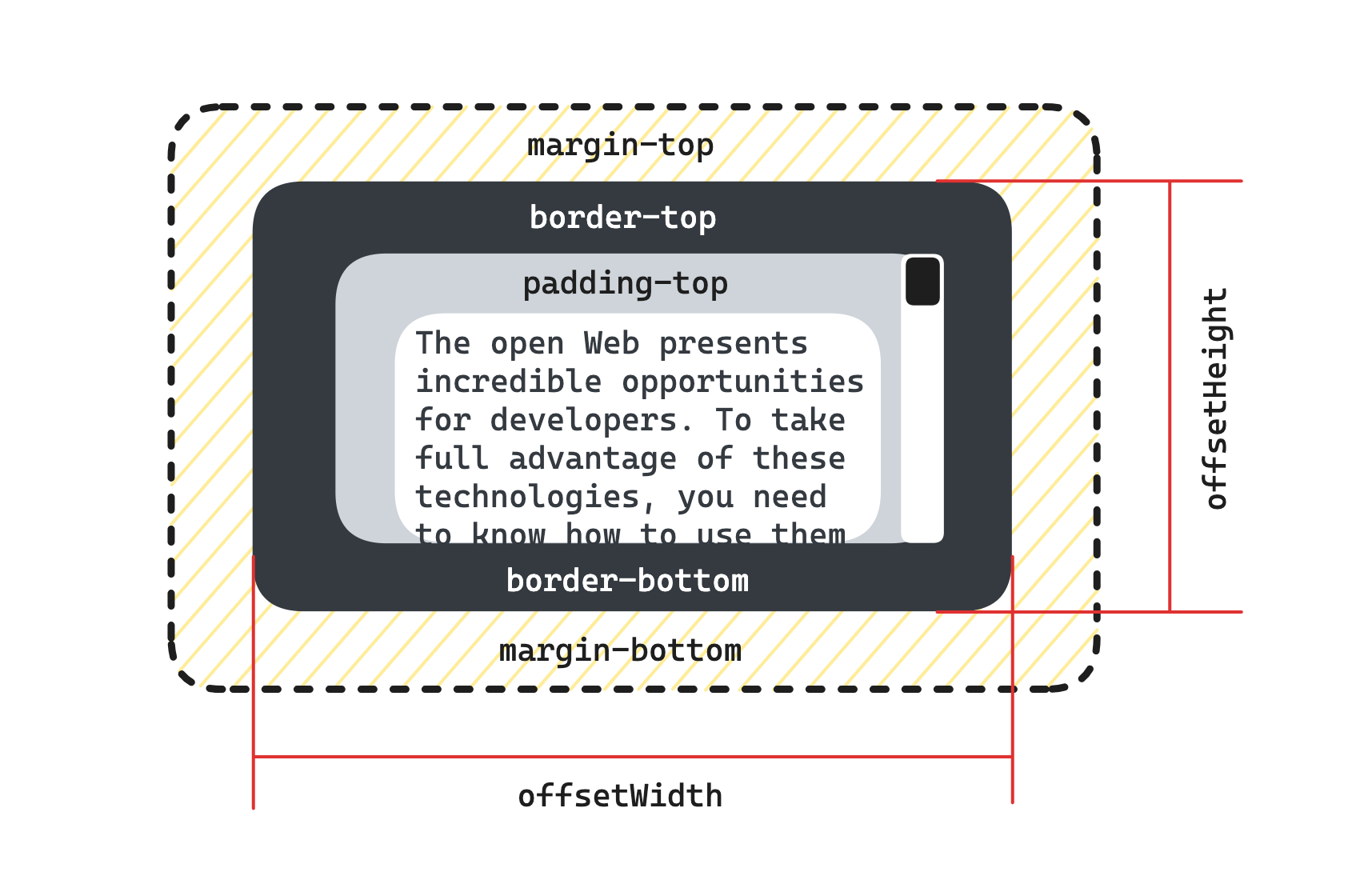
offsetHeight/offsetWidth
HTMLElement.offsetHeight 是一个只读属性,它返回该元素的像素高度,高度包含该元素的垂直内边距和边框,且是一个整数。
通常,元素的 offsetHeight 是一种元素 CSS 高度的衡量标准,包括元素的边框、内边距和元素的水平滚动条(如果存在且渲染的话),不包含:before 或:after 等伪类元素的高度。
如果元素被隐藏(例如 元素或者元素的祖先之一的元素的 style.display 被设置为 none),则返回 0
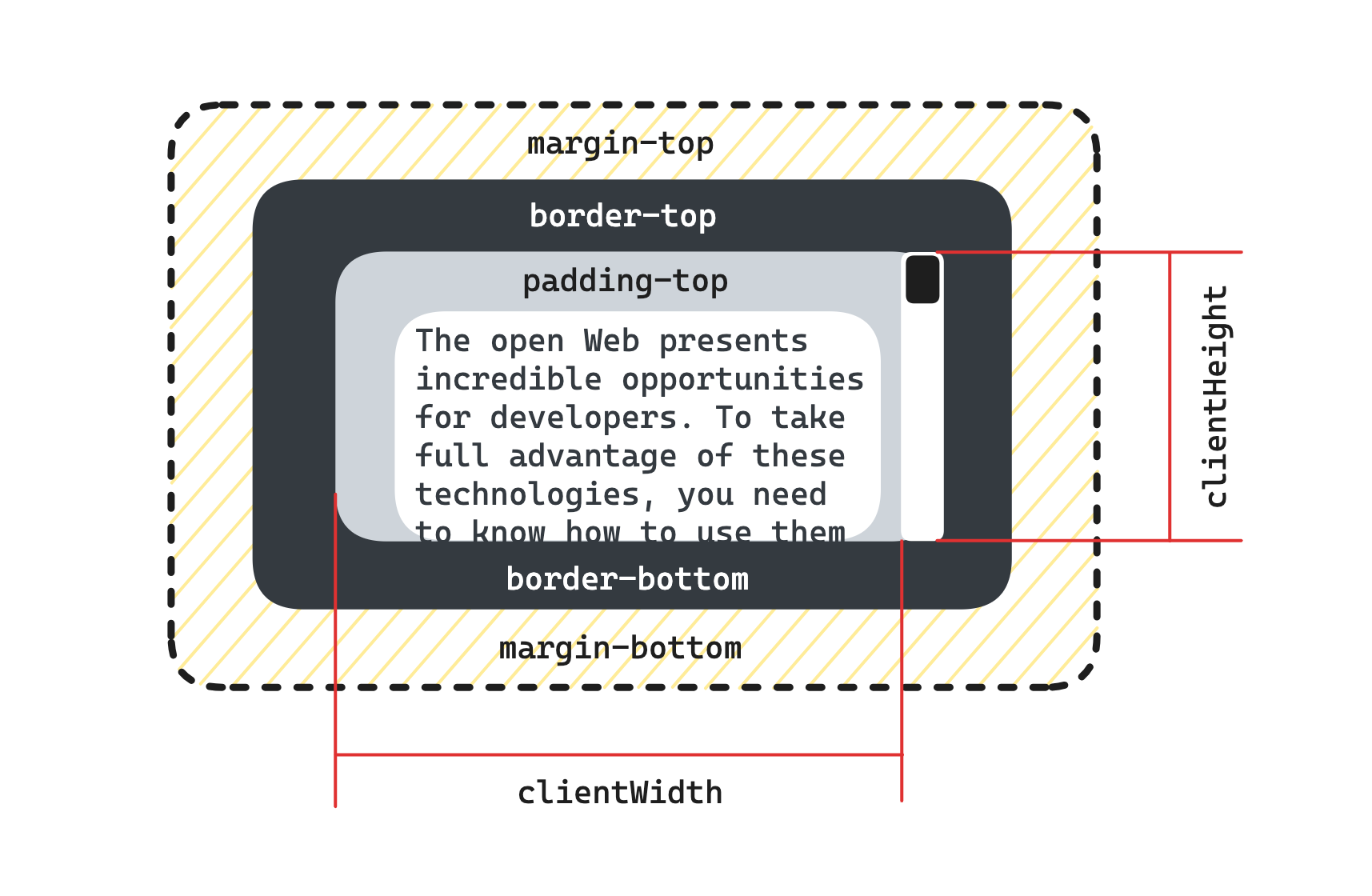
clientHeight/clientWidth
只读属性 Element.clientHeight 对于没有定义 CSS 或者内联布局盒子的元素为 0;否则,它是元素内部的高度(以像素为单位),包含内边距,但不包括边框、外边距和水平滚动条(如果存在)。
clientHeight 可以通过 CSS height + CSS padding - 水平滚动条高度(如果存在)来计算。
在根元素(<html> 元素)或怪异模式下的 <body> 元素上使用 clientHeight 时,该属性将返回视口高度(不包含任何滚动条)。这是一个 clientHeight 的特例。
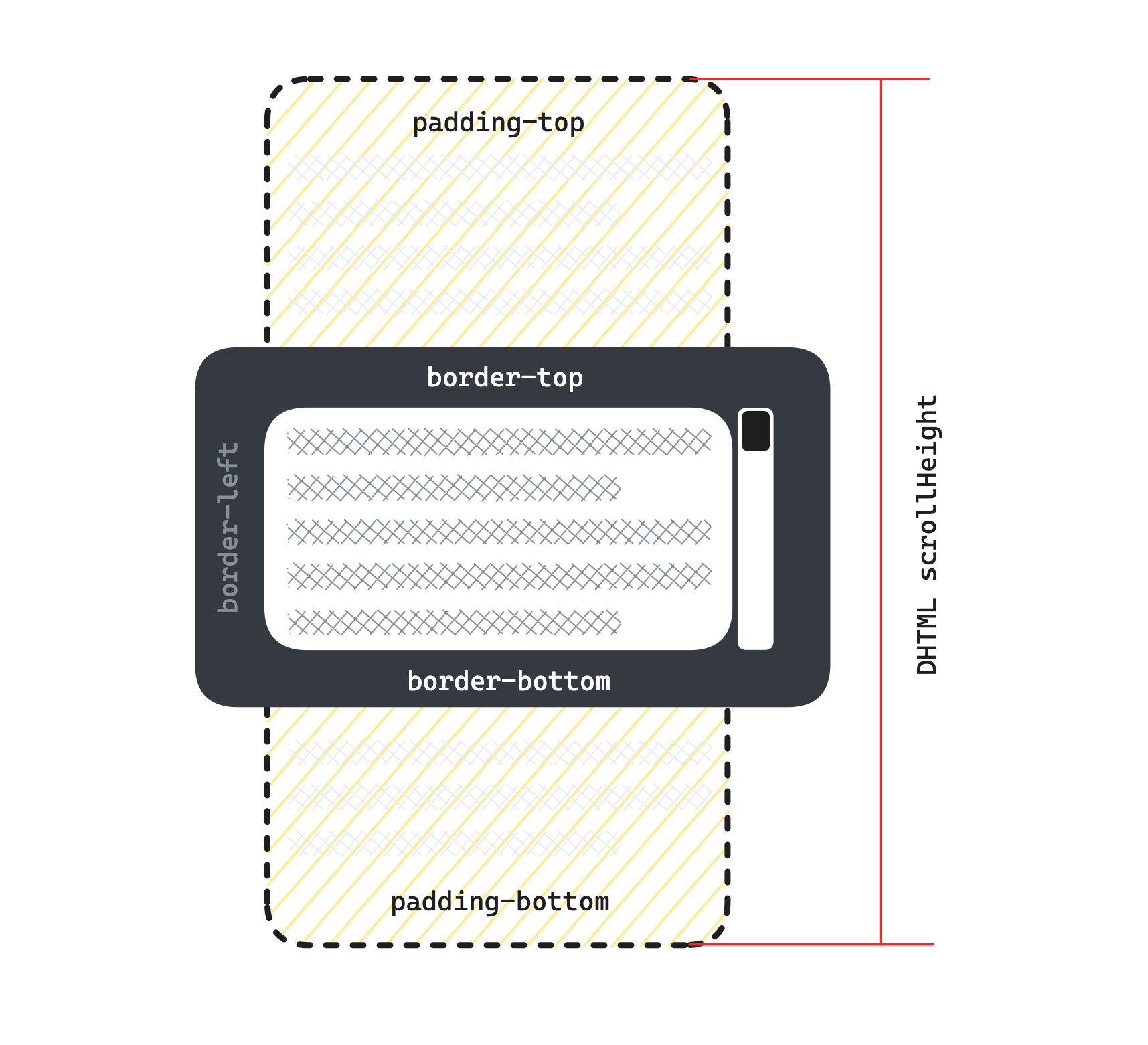
Element.scrollHeight 这个只读属性是一个元素内容高度的度量,包括由于溢出导致的视图中不可见内容。
scrollHeight 的值等于该元素在不使用滚动条的情况下为了适应视口中所用内容所需的最小高度。没有垂直滚动条的情况下,scrollHeight 值与元素视图填充所有内容所需要的最小值clientHeight相同。包括元素的 padding,但不包括元素的 border 和 margin。scrollHeight 也包括 ::before 和 ::after这样的伪元素。 如果元素的内容不需要垂直滚动条就可以容纳,则其 scrollHeight 等于 clientHeight
getComputedStyle
Window.getComputedStyle()方法返回一个对象,该对象在应用活动样式表并解析这些值可能包含的任何基本计算后报告元素的所有 CSS 属性的值。 getComputedStyle返回的对象是只读的。
let style = window.getComputedStyle(element, [pseudoElt]);
getComputedStyle 可以从伪元素拉取样式信息 (比如,::after, ::before, ::marker, ::line-marker—查看 详情 这里).
window.getComputedStyle(element, "::after");
getBoundingClientRect()
Element.getBoundingClientRect() 方法返回一个 DOMRect 对象,其提供了元素的大小及其相对于视口的位置。
DOMRect 对象,是包含整个元素的最小矩形(包括 padding 和 border-width)。该对象使用 left、top、right、bottom、x、y、width 和 height 这几个以像素为单位的只读属性描述整个矩形的位置和大小。除了 width 和 height 以外的属性是相对于视图窗口的左上角来计算的。
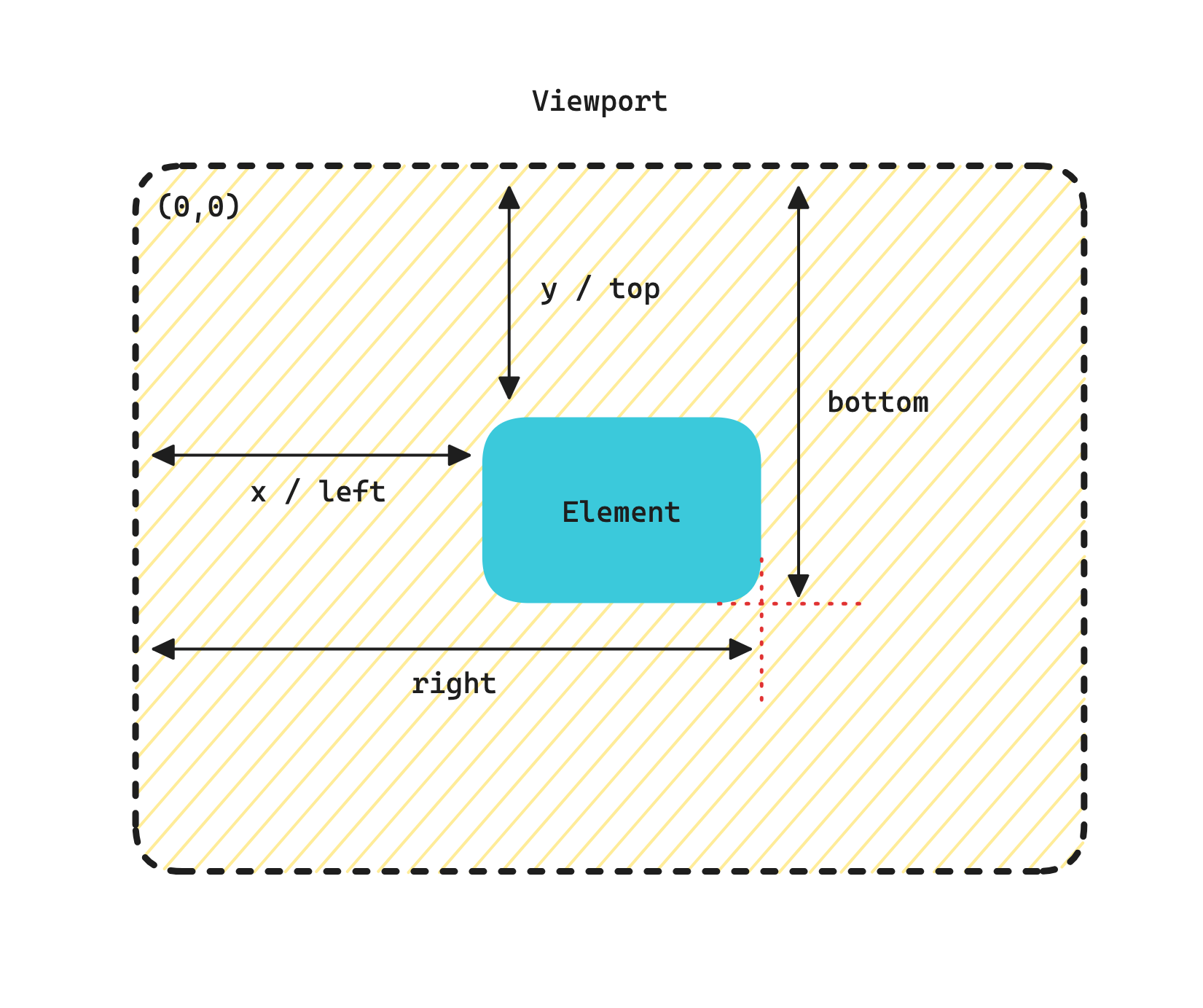
该方法返回的 DOMRect 对象中的 width 和 height 属性是包含了 padding 和 border-width 的,而不仅仅是内容部分的宽度和高度。在标准盒子模型中,这两个属性值分别与元素的 width/height + padding + border-width 相等。而如果是 box-sizing: border-box,两个属性则直接与元素的 width 或 height 相等。
这些方法有什么区别
- offsetHeight:可以用来计算元素的物理空间,此空间包括内容,
padding 和 border(还包括滚动条的宽度,但大多时候滚动条的宽度是计算到 padding 和内容中的)。
- scrollHeight:用来计算可滚动容器的大小,包括不可见的部分,比如一个
300*300 的容器放入一个 600*600 的图片,此时 scrollHeight 为 600,当然,scrollHeight 的值需要加上 padding 的值。
- clientHeight:表示可视区域,包括内容和
padding ,如果有滚动条,还需要减去滚动条的宽度。
- getComputedStyle:获取元素最终尺寸,是元素在浏览器渲染中的最终样式反馈。
- getBoundingClientRect:通常被用来获取元素的位置,
DOMRect 信息。
import { useEffect, useRef, useState } from "react";
const boxStyle = {
backgroundColor: "skyblue",
padding: "20px",
border: "10px solid orange",
height: "200px",
width: "200px"
};
const innerBoxStyle = {
backgroundColor: "rgba(160, 116, 196, 0.8)",
width: "100%",
height: "100%"
};
export default function App() {
const boxRef = useRef<HTMLDivElement>(null);
const [boxSizing, setBoxSizing] = useState<"content-box" | "border-box">(
"content-box"
);
const [rectData, setRectData] = useState({});
const handleToggleBoxSizing = () => {
if (boxSizing === "border-box") {
setBoxSizing("content-box");
} else {
setBoxSizing("border-box");
}
};
useEffect(() => {
if (boxRef.current) {
const rectDetail = boxRef.current.getBoundingClientRect();
setRectData({
height: boxRef.current.style.height,
width: boxRef.current.style.width,
offsetHeight: boxRef.current.offsetHeight,
offsetWidth: boxRef.current.offsetWidth,
clientHeight: boxRef.current.clientHeight,
clientWidth: boxRef.current.clientWidth,
scrollHeight: boxRef.current.scrollHeight,
scrollWidth: boxRef.current.scrollWidth,
getComputedStyle: {
height: window
.getComputedStyle(boxRef.current)
.getPropertyValue("height"),
width: window
.getComputedStyle(boxRef.current)
.getPropertyValue("width")
},
getBoundingClientRect: {
height: rectDetail.height,
width: rectDetail.width
}
});
}
}, [boxRef, boxSizing]);
return (
<div className="p-2">
<div>
<button class="bg-orange-500 text-white p-1 mr-3" onClick={handleToggleBoxSizing}>Toggle Box Sizing Mode</button>
<span>{boxSizing}</span>
</div>
<div className="h-72 mt-3">
<div ref={boxRef} style={{...boxStyle, boxSizing}}>
<div style={innerBoxStyle}></div>
</div>
</div>
<pre class="leading-7">
{JSON.stringify(rectData, undefined, 4)}
</pre>
</div>
);
}
实现 collapse
<template>
<div class="p-4">
<button
class="px-4 py-1 bg-orange-500 border border-orange-500 hover:bg-orange-500/90 text-white mb-4"
@click="handleSwitch"
>
Toggle Content Visibility
</button>
<div
v-show="visible"
ref="collapseRef"
:class="[animating ? 'overflow-hidden' : '']"
:style="collapseStyle"
>
<div class="p-5 bg-gray-200 rounded-xl max-w-2xl">
<div class="text-2xl mb-2">Collapsible Content</div>
<div class="text-xl text-gray-500 leading-7"
>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Sint nam
illum cum sequi totam neque excepturi enim repellendus inventore rerum
quod iusto eligendi, itaque autem nostrum reiciendis assumenda dolore
commodi fuga quisquam veniam aperiam. Perspiciatis tenetur
necessitatibus qui consequuntur molestiae, aliquid illum, nam quod
deserunt animi commodi.</div
>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { defineComponent, computed, ref, nextTick } from 'vue';
function betweenTo(
start,
end,
duration,
doCb,
endCb
) {
const change = end - start;
let startTime = null;
const run = (now) => {
if (!startTime) {
startTime = now;
}
let progress = now - startTime;
if (progress > duration) {
progress = duration;
}
const val = Number.parseInt(
String((progress / duration) * change + start),
10
);
doCb(val);
if (progress < duration) {
window.requestAnimationFrame(run);
} else {
endCb && endCb();
}
};
window.requestAnimationFrame(run);
}
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
setup() {
const collapseRef = ref(null);
const visible = ref(false);
const collapseRefHeight = computed(
() => (collapseRef.value && collapseRef.value.offsetHeight) || 0
);
const animating = ref(false);
const collapseHeight = ref(0);
const collapseStyle = computed(() => {
const result = {};
if (!animating.value) return result;
if (collapseHeight.value > 0) {
result.height = collapseHeight.value + 'px';
} else {
result.visibility = 'hidden';
}
return result;
});
function changeAnimation(v) {
if (animating.value) return;
if (v) {
animating.value = true;
visible.value = v;
nextTick(() => {
betweenTo(
0,
collapseRefHeight.value,
200,
(val) => {
collapseHeight.value = val;
},
() => {
animating.value = false;
}
);
});
} else {
animating.value = true;
betweenTo(
collapseRefHeight.value,
0,
200,
(val) => {
collapseHeight.value = val;
},
() => {
animating.value = false;
visible.value = v;
}
);
}
}
const handleSwitch = () => {
changeAnimation(!visible.value);
};
return {
collapseRef,
visible,
animating,
collapseHeight,
collapseStyle,
handleSwitch
}
}
})
</script>


